CONSERWA
Evidence-based support for transition to agroecological weed management in diverse farming systems and European regions
About Conserwa
26 partners from 12 European countries
Objectives in pillars

Objective 1
Compiling a portfolio of agroecological farming practices, studying their optimal combinations & transferability, including suitability under climate change scenarios.

Objective 2
Supporting the implementation of optimal combinations and measuring their performance & impacts using novel tools.
Objective 3
Supporting knowledge management & communication between stakeholders with the ultimate goal of practical decision-making and impact assessment through an open DSS.

Objective 4
Studying factors influencing farmers’ decision-making in applying agroecological farming, working together with the value chain, such as the food processors & consultancy services.
Work Packages
WP1: Project Management
WP1 coordinates the project tasks, milestones and deliverables, and ensure compliance with EC financial and administrative procedures.
WP2: The CONSERWA case studies
WP2 sets up the case studies and provides grounds for continued data collection, and comparable results on the agro-technical and socio-economic context in each case study
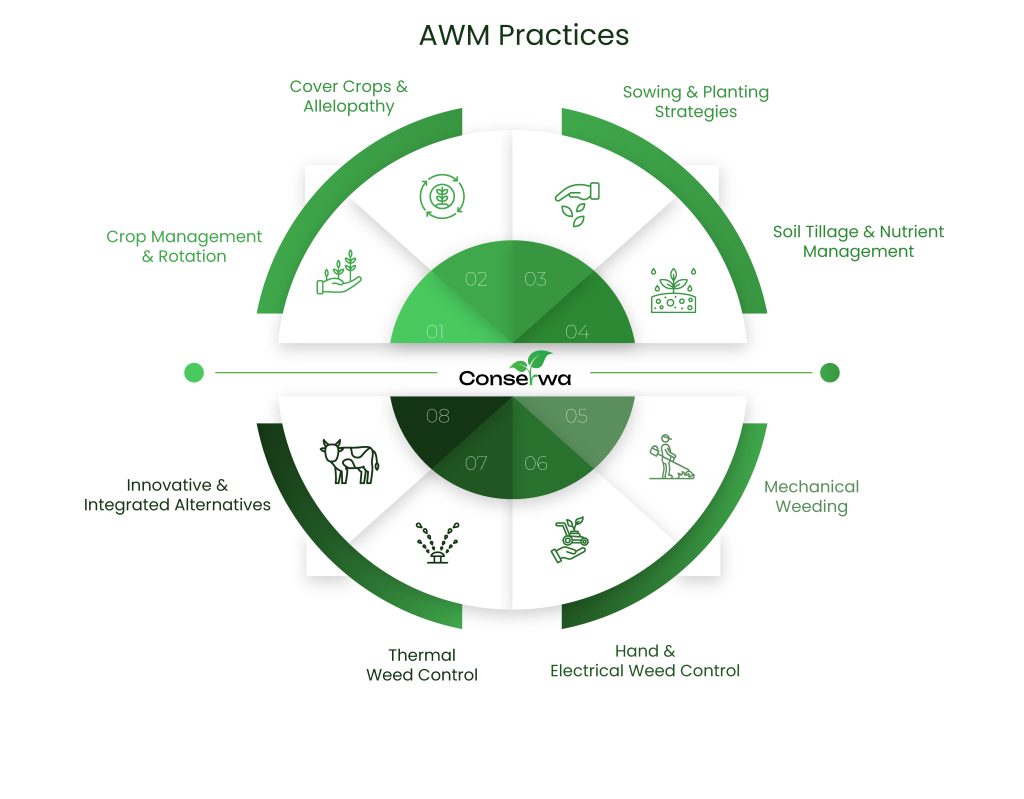
WP3: Agroecological Weed Management practices study and delivery of optimal combinations for the Case Studies
WP3 puts together a library of weed management practices fordifferent crops, farming systems and soil/climate types based on agroecological principles and selects appropriate combinations for each case study, while creating transferability information.
WP4: DSS platform
WP4 develops a Decision Support System, directed to different stakeholders and actors in the value chains for weed management strategies evaluation and selection in agroecological contexts.
WP5: Studying social and system factors influencing adoption of agroecological weed management
WP5 supports continuous engagement of farmers and other important stakeholders (food industry, advisory services, agri-pharma industry, consumers), supports co-design activities while studying factors influencing the adoption of agroecological weed management and the limitation of identified barriers.
WP6: Performance, impact and sustainability assessments
WP6 monitors and assesses the performance of the CONSERWA interventions, their sustainability and impact, as well as the performance of the technology solutions and studies climate change impacts on AWM practices, through the selection of existing KPIs and proposition of new indicators.
WP7: Dissemination, Networking, Training and Exploitation
WP7 facilitates dialogue between farmers and their communities, engages with decision/policy makers, influences industries and society to promote the sharing of knowledge on potential developments in agroecological weed management, while designing and implementing a training program. All project communications, networking, clustering and broader dissemination are monitored in this WP.
Multi-actor approach
CONSERWA utilises the multi-actor approach by

Continuous engagement of farmers and farmer communities in co-designing the CS interventions and in surveys for understanding the barriers they face in adopting AWM practices

Engagement of the food industry through the survey, interviews and focus groups

Setting up consumer observatories to get perspectives on agroecological farming and related products

Involving agri-pharma and IBMA in the design of transition pathways and alternative consultation services

Collaborating with all stakeholders and policy-makers in the preparation of policy recommendations

Engaging with young generation of farmers for training activities
Case studies
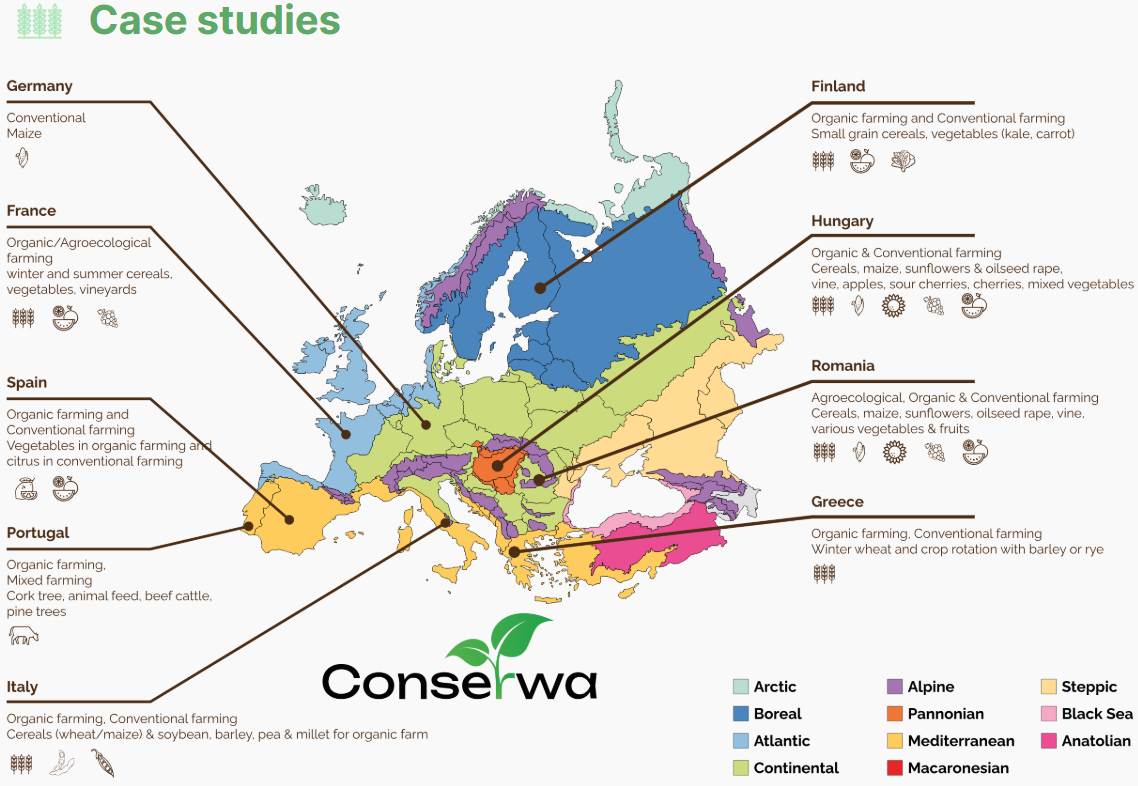
CS 2 – Spain
Pedo-Climatic region: Alpine and Mediterranean
Farming system: Organic farming and Conventional farming
Crops involved: vegetables in organic farming and citrus in conventional farming
CS 3 – Finland
Pedo-Climatic region: Boreal and Arctic
Farming system: Organic farming and Conventional farming
Crops involved: small grain cereals, vegetables (kale, carrot)
CS 4 – Portugal
Pedo-Climatic region: Mediterranean
Farming system: Organic farming, Mixed farming
Crops involved: cork tree, animal feed, beef cattle, pine trees
CS 6 – Hungary
Pedo-Climatic region: Pannonian
Farming system: Organic and Conventional farming
Crops involved: cereals, maize, sunflowers and oilseed rape, vine, apples, sour cherries, cherries, mixed vegetables)
CS 7 – Romania
Pedo-Climatic region: Pannonian, Steppic
Farming system: Agroecological, Organic & Conventional farming
Crops involved: cereals, maize, sunflowers, oilseed rape, vine, various vegetables & fruits
CS 9 – Germany
Pedo-Climatic region: Continental & Atlantic
Farming system: Conventional
Crops involved: maize
Triple Performance

The project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 101081802